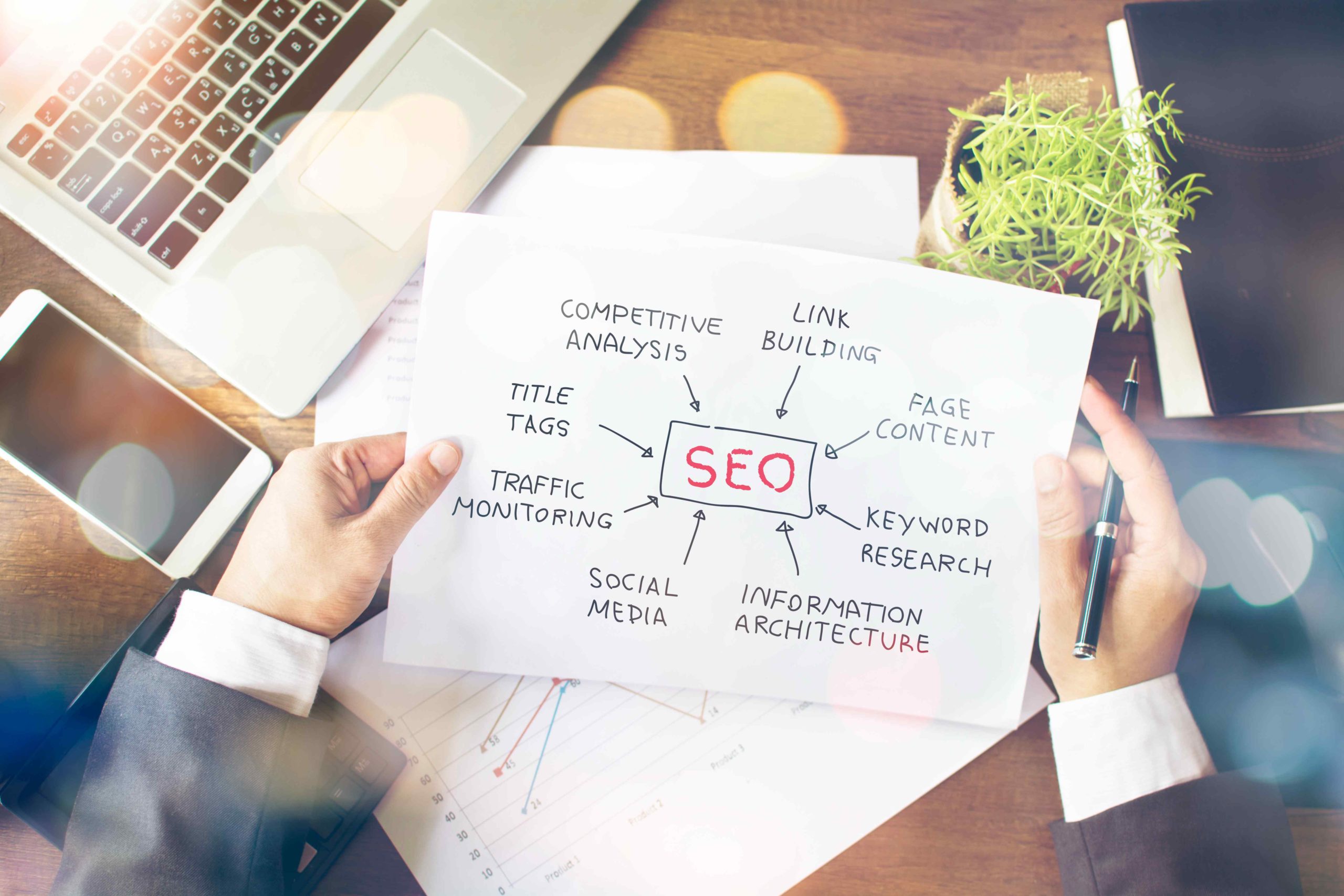
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility and ranking in search engine results. It’s a crucial component of any successful digital marketing strategy, and it’s something that every website owner should be focusing on.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of on-page SEO, exploring the key elements that you need to master in order to drive more traffic, generate more leads, and ultimately, grow your business.
What Exactly is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. It involves optimizing both the content and HTML source code of a page.
The goal of on-page SEO is to make it easy for both search engines and users to:
- Understand what a webpage is about
- Identify the page as relevant to specific search queries
- Find the page useful and worthy of ranking well in search results
The Importance of On-Page SEO
Here are the key reasons why on-page SEO is important:
- Improved search engine understanding: On-page SEO helps search engines analyze and understand your website’s content, making it easier to determine its relevance to specific search queries.
- Higher rankings: By optimizing various on-page elements, you increase the chances of your website ranking higher in search results for relevant keywords.
- Increased organic traffic: Better rankings lead to more visibility, which can result in increased organic traffic to your website.
- Better user experience: Many on-page SEO techniques, such as improving page load speed and mobile-friendliness, also enhance the overall user experience. Check out our article How User Experience Affects SEO.
- Targeted content: On-page SEO encourages the creation of high-quality, relevant content that addresses user intent and satisfies searchers’ needs.
- Competitive advantage: Proper on-page optimization can help your website outrank competitors in search results. Learn more in this article: https://quirk.biz/how-to-beat-competitors-at-seo/
- Cost-effective marketing: Compared to paid advertising, on-page SEO offers a better return on investment with long-term benefits.
- Improved click-through rates: Optimizing meta titles and descriptions can lead to higher click-through rates from search results.
- Enhanced site structure: On-page SEO involves optimizing internal linking and site structure, making it easier for both users and search engines to navigate your website.
- Adaptation to algorithm changes: Regular on-page SEO efforts help your website stay up-to-date with evolving search engine algorithms.
By focusing on on-page SEO, you create a strong foundation for your website’s overall search engine optimization strategy, improving its visibility, user experience, and ultimately, its ability to attract and convert potential customers.
How to Use On-Page SEO Techniques: Comprehensive Guide
Publish High-quality, Original Content
By consistently publishing high-quality, original content optimized for search engines and readers, you can improve your on-page SEO and drive more qualified traffic to your site. Remember, quality content is an ongoing process that requires significant effort, but it’s one of the most effective ways to achieve long-term SEO success.
Here are some key points to consider when creating and publishing original content:
- Focus on value and uniqueness: Create content that offers new insights, perspectives, or information not readily available elsewhere. Aim to provide genuine value to your readers.
- Address user intent: Understand what your audience is searching for and create content that directly answers their questions or solves their problems.
- Demonstrate expertise: Showcase your knowledge and experience in your field. Share original research, case studies, or expert opinions to establish authority.
- Use a variety of content formats: Incorporate different types of media such as images, videos, infographics, and interactive elements to enhance engagement and provide a richer user experience.
- Maintain consistency: Regularly publish fresh, original content to keep your audience engaged and signal to search engines that your site is active and relevant.
- Optimize for readability: Use clear, concise language and structure your content with headers, short paragraphs, and bullet points to make it easy to read and scan.
- Incorporate relevant keywords: While focusing on originality, naturally include relevant keywords to help search engines understand your content’s topic and relevance. I recommend our article How to Do Keyword Research for SEO for expert tips and insights.
- Encourage engagement: Include calls-to-action, ask questions, or invite comments to encourage reader interaction and build a community around your content.
- Update existing content: Regularly review and update your published content to ensure it remains accurate, relevant, and valuable over time.
- Promote your content: Share your original content across various platforms and channels to increase its visibility and reach a wider audience.
Optimize Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
Optimizing page titles and meta descriptions is a crucial on-page SEO technique that can improve your search engine rankings and drive more qualified traffic to your site.
Here’s how to optimize these elements:
- Include target keywords: Conduct keyword research to identify the main keyword phrase for each page. Include this keyword naturally in the page title, ideally towards the beginning. Also incorporate the keyword or its variations in the meta description. However, avoid keyword stuffing as it can hurt your rankings.
- Write compelling, click-worthy titles: Craft page titles that not only include keywords but also entice users to click. Use power words, emotional triggers, or numbers to make titles more compelling. For example, “10 Proven Techniques to Boost Your SEO Rankings in 2023” is more engaging than simply “SEO Ranking Tips.”
- Keep title length under 60 characters: Search engines typically display the first 50-60 characters of a page title. Keep your titles under 60 characters to prevent them from being cut off in search results. Put the most important keywords and phrases towards the beginning.
- Optimize title format: Use a clear and descriptive title format that includes the main keyword and your brand name, such as “Primary Keyword – Secondary Keyword | Brand Name.” This helps search engines understand the page’s topic and associates it with your brand.
- Write unique titles for each page: Avoid duplicating page titles across your site. Each page should have a unique, specific title that accurately reflects its content. Duplicate titles can confuse search engines and dilute the relevance of your pages.
- Craft informative, engaging meta descriptions: Meta descriptions, while not a direct ranking factor, can significantly impact click-through rates from search results. Write compelling descriptions that clearly summarize the page’s content, include the main keyword, and encourage users to click. Aim for around 150-160 characters.
- Match search intent: Ensure that your page titles and meta descriptions align with the user’s search intent. Understand what information or solution users are looking for when searching for your target keyword, and optimize your titles and descriptions accordingly.
- Use action-oriented language: Incorporate action words and phrases in your meta descriptions to encourage clicks. For example, “Discover the secrets to…” or “Learn how to…” can entice users to click through to your page.
- Highlight unique value propositions: Use your page title and meta description to showcase what sets your content apart. Highlight unique selling points, benefits, or offerings that make your page the best result for the user’s query.
- Monitor and adjust: Track your page’s performance in search results and adjust titles and descriptions as needed. Use tools like Google Search Console to monitor click-through rates and search rankings. Continuously optimize based on data to improve your results over time.
Use Header Tags to Structure Content
By using header tags to structure your content effectively, you can improve your on-page SEO, make your content more user-friendly, and help search engines better understand the main topics and hierarchy of your web pages. This can lead to higher search rankings, increased traffic, and better engagement with your content.
Here’s how to effectively use header tags to structure your content:
- Use a single H1 tag for the main title: The H1 tag should be used only once per page to indicate the main title or heading of the content. It should include the primary keyword you’re targeting and clearly describe what the page is about. Avoid using generic H1 tags like “Home” or “Products.”
- Use H2 tags for main sections: H2 tags serve as subheadings to break up the content into main sections. They provide a high-level overview of the key topics covered on the page. Use descriptive, keyword-rich H2 tags to help search engines and users understand the main points.
- Use H3-H6 tags for further subsections: H3 to H6 tags create a hierarchical structure within the H2 sections. They help organize the content into smaller, more specific subsections. Use them to group related ideas and improve the readability of your content.
- Keep heading tags consistent and descriptive: Maintain a consistent heading structure throughout the page. Don’t skip levels (e.g., going from H2 to H4) as this can confuse users and search engines. Keep headings descriptive and concise, ideally under 70 characters.
- Incorporate keywords in heading tags: Include relevant keywords in your heading tags where appropriate, but avoid overusing them. Focus on creating informative, engaging headings that accurately reflect the content. Use variations and long-tail keywords to optimize for different search queries.
- Use heading tags to improve readability: Heading tags make your content more scannable and easier to read. They help users quickly grasp the main points and find the information they’re looking for. Use headings to break up long blocks of text and make your content more visually appealing.
- Ensure heading tags follow a logical hierarchy: The heading structure should follow a logical order, with H2s representing the most important topics, H3s representing subtopics within H2s, and so on. This helps create a clear outline and makes it easier for search engines to understand the content’s structure.
- Use CSS to style heading tags consistently: Use CSS to ensure heading tags are visually distinct and consistently styled across your site. This enhances usability and makes it easier for users to recognize the hierarchy of the content.
Optimize Images
By optimizing your images, you can improve your website’s SEO, reduce page load times, and provide a better user experience for your visitors. Optimized images can help your content rank higher in both Google Images and regular search results, driving more qualified traffic to your site.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to optimize images for SEO:
- Choose relevant, high-quality images: Select images that are relevant to your content and support your message. Use original, high-quality images whenever possible, as they can help you stand out from competitors using generic stock photos. Unique images are also more likely to attract backlinks.
- Use appropriate image formats: Choose the right file format for your images:
– JPEG for photographs and complex images with many colors
– PNG for images with transparency, text, or simple graphics
– SVG for logos, icons, and simple illustrations that need to scale
– WebP as a modern format that offers superior compression
- Compress images: Reduce image file sizes through compression to improve page load speed, a key ranking factor. Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or plugins like Smush to compress images without noticeable quality loss. Aim to keep images under 100KB.
- Resize images: Scale images to the appropriate dimensions for your website layout. Avoid uploading unnecessarily large images and then resizing them with HTML or CSS, as this still impacts page load time. Resize images before uploading them to your site.
- Use descriptive file names: Name your image files with descriptive, keyword-rich names that give search engines context about the image content. Use hyphens to separate words (e.g., “blue-widget.jpg”) instead of underscores or spaces.
- Optimize alt text: Add descriptive, keyword-rich alt text to every image. Alt text helps search engines understand the content of the image and is used by screen readers for visually impaired users. Keep alt text concise (under 125 characters) and avoid keyword stuffing.
- Include captions: Add informative captions below images when appropriate. Captions provide additional context for users and can include relevant keywords for search engines.
- Use responsive images: Ensure your images are responsive and adapt to different screen sizes and devices. Use the HTML srcset attribute or CSS media queries to serve images of appropriate sizes based on the user’s device.
Optimize URLs
By optimizing URLs, you can create SEO-friendly URLs that are easier for both users and search engines to understand, improving your site’s visibility and organic traffic.
Here’s how to create SEO-friendly URLs:
- Use descriptive, keyword-rich URLs: Create URLs that accurately describe the page’s content and include relevant keywords. This helps both users and search engines understand what the page is about.
- Keep URLs short: Shorter URLs are easier to read, remember, and share. Aim to keep URLs under 100 characters when possible. Remove unnecessary words like “and”, “the”, “of”, etc..
- Use hyphens to separate words: Use hyphens (-) to separate words in your URL. Avoid using underscores (_), spaces, or other special characters. Search engines treat hyphens as word separators, making the URL more readable.
- Use lowercase letters: Use all lowercase letters in your URLs. Mixed case URLs can lead to duplicate content issues, as search engines treat “page1” and “Page1” as different URLs.
- Place important keywords towards the beginning: Put the most important keywords at the beginning of the URL. Search engines give more weight to words at the start of the URL.
- Avoid keyword stuffing: While including keywords is important, avoid overusing them in your URLs. Stuffing too many keywords can appear spammy to both users and search engines.
- Use static URLs when possible: Static URLs are easier for search engines to crawl and tend to rank better than dynamic URLs with multiple parameters (?=&). Avoid unnecessary parameters when possible.
- Match URLs to page titles: When possible, match your URL to your page title. This reinforces the page’s topic and makes it easier for users to remember.
- Use a flat directory structure: Keep your URL structure as flat as possible. Avoid deep nesting of subdirectories, as this can make URLs longer and less user-friendly.
- Canonicalize URLs: Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a URL if you have multiple versions of the same page (e.g., with parameters or www vs. non-www). This helps avoid duplicate content issues.
- Redirect old URLs: If you change a page’s URL, use a 301 redirect to point the old URL to the new one. This ensures any link equity from the old URL is passed to the new one.
Use Internal Links
Internal linking is an SEO technique that involves linking one page on your website to another relevant page within the same domain. By using internal links, you can create a strong site architecture, boost your pages’ authority, and improve your overall search engine rankings.
Here’s a how to use internal linking for SEO:
- Create a logical site structure: Organize your website into a clear, hierarchical structure with main categories and subcategories. This makes it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your site, and for users to navigate.
- Link to your most important pages: Identify your key pages (e.g., cornerstone content, product pages) and link to them from relevant pages on your site. This helps pass link equity (authority) to these important pages and can improve their search rankings.
- Use relevant, descriptive anchor text: When linking internally, use anchor text that accurately describes the content of the linked page. This helps search engines understand the context and topic of the linked page. Avoid generic phrases like “click here”.
- Link deep within your site: Don’t just link to your homepage or top-level pages. Link to deeper, more specific pages as well. This helps search engines discover and index all your content and can improve the authority of inner pages.
- Use a reasonable number of internal links: While internal links are beneficial, don’t overdo it. Aim for a natural balance – around 5-10 internal links per 2,000 words is a good guideline. Too many links can dilute their value and appear spammy.
- Audit your internal links regularly: Use tools like Google Search Console or Semrush to analyze your site’s internal linking structure. Look for issues like broken links, pages with too few links, or unimportant pages with too many links. Fix these issues to optimize your internal linking.
- Use internal linking to improve user experience: In addition to SEO benefits, internal links help users navigate your site and find related content. Link to relevant pages that provide additional value and keep users engaged on your site longer.
- Leverage high-authority pages: If you have pages with strong backlink profiles and high PageRank, link from these pages to other important pages you want to boost. This passes link equity and can improve the linked pages’ search performance.
- Use internal linking to distribute PageRank: PageRank is Google’s algorithm for measuring a page’s importance. By strategically linking from high-authority pages to other key pages, you can distribute PageRank throughout your site and improve overall rankings.
- Keep your internal linking natural: Avoid over-optimizing your internal links or using exact-match anchor text excessively. Use internal links where they make sense for users and fit naturally in your content. Aim for a diverse range of anchor text phrases.
Use External Links
External linking is an important on-page SEO technique that involves linking to other relevant, high-quality websites from your own content. When used strategically, external linking can enhance your content’s value, improve user experience, and indirectly benefit your search rankings. By linking to reputable sources, you demonstrate your site’s credibility and encourage other authoritative sites to link back to your content, strengthening your overall SEO.
Here’s our guide on how to use external linking for SEO:
- Link to relevant, authoritative sources: When linking to external websites, choose sites that are reputable and relevant to your content. Linking to high-quality sources helps establish your site’s credibility and trustworthiness. Use accurate, descriptive anchor text that reflects the linked page’s content.
- Use external links to provide additional value: Include external links that offer complementary information or resources that enhance your content’s value to readers. These links should provide more depth or context to the topic you’re discussing. Aim to link to content that your audience will find helpful and interesting.
- Be selective with external links: Avoid including too many external links, especially within a single paragraph or sentence. Too many outbound links can distract readers and dilute the impact of each individual link. Focus on including only the most relevant and valuable external resources.
- Set external links to open in new windows: Configure external links to open in new browser windows or tabs. This keeps visitors on your site even if they click an external link, reducing bounce rates and encouraging them to continue engaging with your content.
- Regularly audit and update external links: Websites can change URLs, remove pages, or shut down entirely. Periodically check your outbound links to ensure they’re still functional and pointing to relevant, high-quality resources. Broken external links can frustrate users and negatively impact SEO. Use tools to monitor your site’s external links and promptly fix any issues.
- Use external links to build relationships: Linking to other websites can help initiate link-building relationships. Reach out to the sites you’ve referenced to let them know you’ve included their content. They may reciprocate by sharing your content or linking back to your site, boosting your own external link profile.
Also, check out our article about selling backlinks, to learn more useful information.
Improve page load speed
Improving page load speed is an important on-page SEO technique that can boost your search engine rankings, enhance user experience, and increase conversions.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to optimize your page load speed:
- Optimize images: We already mentioned this above, but it’s important to remember this: images are often the largest files on a webpage. That’s why it is necessary to compress images using tools like TinyPNG or Kraken.io to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality. Use appropriate image formats (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with transparency, SVG for simple icons). Specify image dimensions to prevent layout shifts during loading.
- Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Minification removes unnecessary characters (whitespace, comments) from code, reducing file sizes. Use tools like HTMLMinifier, CSSNano, or UglifyJS to automate the process. Smaller files load faster.
- Leverage browser caching: Browser caching stores static files (images, CSS, JavaScript) locally on the user’s device, so they don’t need to be re-downloaded on subsequent visits. Set appropriate cache headers (e.g., Cache-Control, Expires) to specify how long files should be cached.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN): CDNs distribute your content across a network of servers worldwide. Users receive content from the server closest to their location, reducing latency and improving load times. Popular CDNs include Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, and Akamai.
- Optimize server response time: Choose a reliable, performance-focused hosting provider. Optimize your server configuration (e.g., enabling HTTP/2, adjusting TimeToFirstByte). Consider using a caching plugin or server-side caching to generate static HTML files and reduce database queries.
- Minimize redirects: Each redirect adds additional HTTP request-response cycles, slowing down page loading. Minimize the use of redirects, especially on critical paths like the homepage or key landing pages. When necessary, use server-side redirects (HTTP 301) instead of client-side redirects (meta refresh). Learn more about different types of redirects.
- Prioritize above-the-fold content: Structure your HTML to load above-the-fold content first. Use techniques like inline critical CSS and deferred loading of non-critical resources (e.g., below-the-fold images, scripts) to ensure users see content quickly. This improves perceived performance and reduces bounce rates.
- Monitor and analyze performance: Regularly assess your page load speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest. These tools provide performance scores, identify bottlenecks, and offer optimization suggestions. Continuously monitor and improve performance based on these insights.
Make Your Website Mobile-Friendly
As mobile usage continues to grow, having a mobile-optimized site is no longer optional – it’s a necessity for SEO success.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to optimize your site for mobile devices:
- Use responsive web design: Responsive design ensures your website automatically adjusts its layout and content to fit any screen size, from desktops to smartphones. This eliminates the need for a separate mobile site and provides a consistent user experience across devices. Responsive design is Google’s recommended approach for mobile optimization.
- Optimize for touch screens: Design your site with touch screens in mind. Make buttons and links large enough to be easily tapped with a finger. Ensure there’s enough space between clickable elements to avoid accidental clicks. Use legible font sizes that don’t require zooming to read.
- Simplify navigation: Mobile users typically want to find information quickly. Simplify your site’s navigation by using a clear, concise menu structure. Prioritize the most important pages and use descriptive labels. Consider using a hamburger menu icon to save space. Ensure the search function is prominent and returns relevant results.
- Optimize images and videos: Large images and videos can slow down your mobile site. Compress images without sacrificing quality. Use responsive images that adapt to different screen sizes. For videos, consider using a responsive player that adjusts to the device’s dimensions. Provide alternative text for images to help search engines understand their content.
- Minimize pop-ups and interstitials: Pop-ups and interstitials (pages displayed before or after the expected content) can be disruptive on mobile devices. They can cover the entire screen and be difficult to close. Google may penalize sites that use intrusive interstitials. If you must use them, ensure they’re easily dismissible and don’t interfere with the main content.
- Use legible fonts and contrasting colors: Choose fonts that are easy to read on small screens. Avoid using too many different fonts. Ensure there’s sufficient contrast between the text and background colors to improve readability. Google recommends a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1.
- Test on multiple devices: Test your website on various mobile devices and screen sizes to ensure it displays and functions correctly. Use browser developer tools to simulate different devices. Consider using a mobile testing tool like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to identify any issues.
- Implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): AMP is an open-source framework that allows you to create lightweight, fast-loading pages for mobile devices. AMP pages typically load faster than regular mobile pages and may appear in a special carousel in search results. Consider implementing AMP for your key content pages to improve mobile performance.
Use Schema Markup
Schema markup is a powerful on-page SEO technique that helps search engines better understand your content and display rich snippets in search results.
Here’s how to use schema markup for SEO:
- Understand what schema markup is: Schema markup is a type of structured data that you add to your website’s HTML to provide explicit information about your content to search engines. It is a standardized format established by Schema.org, a collaborative effort between Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex.
Schema uses a vocabulary of tags (microdata) to define properties of your content, such as the type of content, author, publication date, ratings, reviews, and more. This additional context helps search engines interpret your content more accurately.
- Identify relevant schema types for your content: There are various schema types available for different kinds of content, such as articles, products, recipes, events, organizations, and local businesses. Identify the schema types that are most relevant to your website’s content. For example, if you have a recipe website, you can use the Recipe schema to markup ingredients, cooking time, nutrition information, and ratings. If you have an e-commerce store, you can use the Product schema to markup details like price, availability, and reviews.
- Choose the appropriate format: Schema markup can be implemented using three formats: JSON-LD, Microdata and RDFa.
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the easiest to implement, as it doesn’t require changes to your HTML. You simply add a script tag with the structured data in the head or body of your page. Google recommends using JSON-LD for schema markup.
- Generate and test your schema markup: Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or Schema Markup Generator to create your schema markup. These tools guide you through the process of tagging your content and generate the corresponding JSON-LD code.
After generating the markup, test it using Google’s Rich Results Test tool. This tool validates your schema and previews how your rich snippets may appear in search results.
- Implement the schema markup on your website: Add the generated JSON-LD script to the head or body of the relevant pages on your website. If you’re using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, you can use plugins like Schema Pro or Schema & Structured Data for WP to simplify the implementation process.
- Monitor your rich snippets: Use Google Search Console’s “Enhancements” report to monitor the performance of your schema markup. This report shows which rich snippets are being generated for your site, as well as any errors or warnings related to your structured data.
- Keep your schema markup up to date: Regularly review and update your schema markup to ensure it accurately reflects your content. As you make changes to your website, such as adding new products or updating recipes, make sure to update the corresponding schema as well.
Optimize for Featured Snippets
Optimizing for featured snippets is an important on-page SEO technique that can help your content appear at the very top of Google’s search results, above the regular organic listings. Featured snippets provide concise, direct answers to user queries and can significantly boost your visibility and organic traffic.
Here’s how to optimize your content for featured snippets:
- Identify question-based queries relevant to your content: Featured snippets often appear for question-based searches that start with “what,” “why,” “how,” “when,” “who,” etc. Use keyword research tools to find common questions related to your topic that have a featured snippet opportunity. Look for queries where you can provide a clear, concise answer.
- Provide direct, concise answers: When creating content, directly answer the target question in a clear, concise manner. Aim for a short paragraph or 2-3 sentence answer that completely addresses the query. This brief answer is what Google will likely pull for the featured snippet.
- Use question-based subheadings: Structure your content with subheadings that mirror the exact question you’re targeting. For example, if you’re targeting “How to optimize for featured snippets,” use that exact phrase as your H2 or H3 subheading. Then, directly below the subheading, provide your concise answer. This makes it easy for Google to identify and extract the relevant information.
- Use ordered and unordered lists: Featured snippets often appear in a list format, especially for “how-to” or step-by-step queries. When creating content, use ordered lists (numbered) for sequential steps and unordered lists (bullets) for related items. Keep the list items concise and informative.
- Aim for the “People also ask” box: In addition to the main featured snippet, Google often shows a “People also ask” box with related questions. Target these questions in your content as well, using a similar format of a clear subheading followed by a concise answer. This increases your chances of appearing in multiple featured snippets for related queries.
Conclusion
By focusing on these on-page SEO elements, you can optimize your content for both search engines and users, improving your chances of ranking higher and attracting more qualified traffic. However, on-page SEO is just one part of a comprehensive SEO strategy that should also include off-page factors like link building and technical considerations like site architecture and crawlability.
It’s an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and updates to ensure your content stays relevant and aligned with evolving search engine algorithms.
While keyword optimization is still important, modern on-page SEO focuses more on overall relevance and meeting user intent rather than just keyword placement or density. It’s about creating valuable content that serves the needs of your target audience while also being optimized for search engines.