In the realm of websites and SEO, “root domain” is a popular term.
As professionals, understanding this concept is key to optimizing how well a site shows up online.
In this brief guide, we’ll explore why root domains matter, how they shape a website’s digital foundation, and their impact on search engine rankings.
Key Takeaways
- A root domain is the main part of your website’s domain name that represents the primary address of a website on the internet. (“example.com”)
- The root domain is the overarching structure containing the subdomains and every URL of a website, while subdomains are smaller parts of the root domain used to organize and categorize content and provide a better user experience. (“shop.example.com”)
- The TLD is the last segment of text in a domain name, indicating the type or category of the website. (“shop.example.com“)
- The root domain is crucial for establishing a brand, creating a professional image, and organizing the website’s content.
Defining the Root Domain
A root domain is the main part of your website’s domain name that represents the primary address of a website on the internet. It is the foundation from which all other subdomains and pages branch out.
For example, in the web address “www.example.com,” “example.com” is the root domain.
It serves as the starting point for users navigating through the site’s hierarchy.
Are Root Domains Important For SEO?
Regarding SEO, it’s important to note that the domain name itself isn’t directly influencing search engine rankings. However, certain aspects of your domain name may impact the overall success of your SEO strategy.
Search engines use complex algorithms to crawl and index web pages, and a well-organized domain structure helps this process.
Here are our advice on optimizing your root domains to improve your SEO:
- Memorability: When choosing a root domain, opt for something that’s easy to read, remember, and pronounce. A user-friendly domain helps both visitors and search engines get the nature of your site, potentially boosting your rankings in relevant search results.
- Length: For an effective online presence, consider keeping your domain name short and specific. Search engines tend to favor such names, so a clear and concise website name can significantly enhance your SEO efforts.
- Keyword Inclusion: Incorporating relevant keywords into your root domain name is key to attracting the right audience. This strategic use of keywords aligns your site with user search intent, improving visibility in search engine results.
- Brand-ability: Choose a root domain name that distinctly represents your brand. This makes it easier for visitors to associate your website with your brand identity, contributing to a strong online presence.
Differences Between Root Domains and Subdomains
Root domains and subdomains are distinct components of a website’s architecture, each serving specific purposes. Here are the key differences between root domains and subdomains:
Definition
- Root Domain: The root domain is the main and highest level of a domain hierarchy. It represents the primary address of a website, such as “example.com.”
- Subdomain: A subdomain is an extension of the root domain, creating additional sections or categories. It precedes the root domain in a URL, like “blog.example.com” or “shop.example.com.”
Structure
- Root Domain: Stands alone as the base of a domain hierarchy, without any prefix.
- Subdomain: Adds a prefix to the root domain, creating a hierarchical structure beneath it.
Functionality
- Root Domain: Typically represents the main website and its primary content.
- Subdomain: Used to create separate sections for specific content or functionalities. For instance, a blog, store, or support section may each have its own subdomain.
SEO Impact
- Root Domain: The overall authority and reputation of the website are associated with the root domain. It plays a crucial role in search engine rankings.
- Subdomain: While it can have its own content and purpose, a subdomain is often treated as a separate entity in terms of SEO. It may not inherit the same level of authority as the root domain.
URL Format
- Root Domain: Appears without any prefix, like “example.com.”
- Subdomain: Appears as a prefix to the root domain, such as “https://blog.example.com” or “shop.example.com.”
Independence
- Root Domain: Represents the main entity; changes to the root domain impact the entire website.
- Subdomain: Operates somewhat independently. Changes to one subdomain may not directly affect others or the root domain.
Common Use Cases
- Root Domain: Used for the main website, company homepage, or primary content.
- Subdomain: Employed for specialized content areas like blogs, forums, e-commerce stores, or support portals.
More about subdomains read here: https://quirk.biz/what-is-a-subdomain/
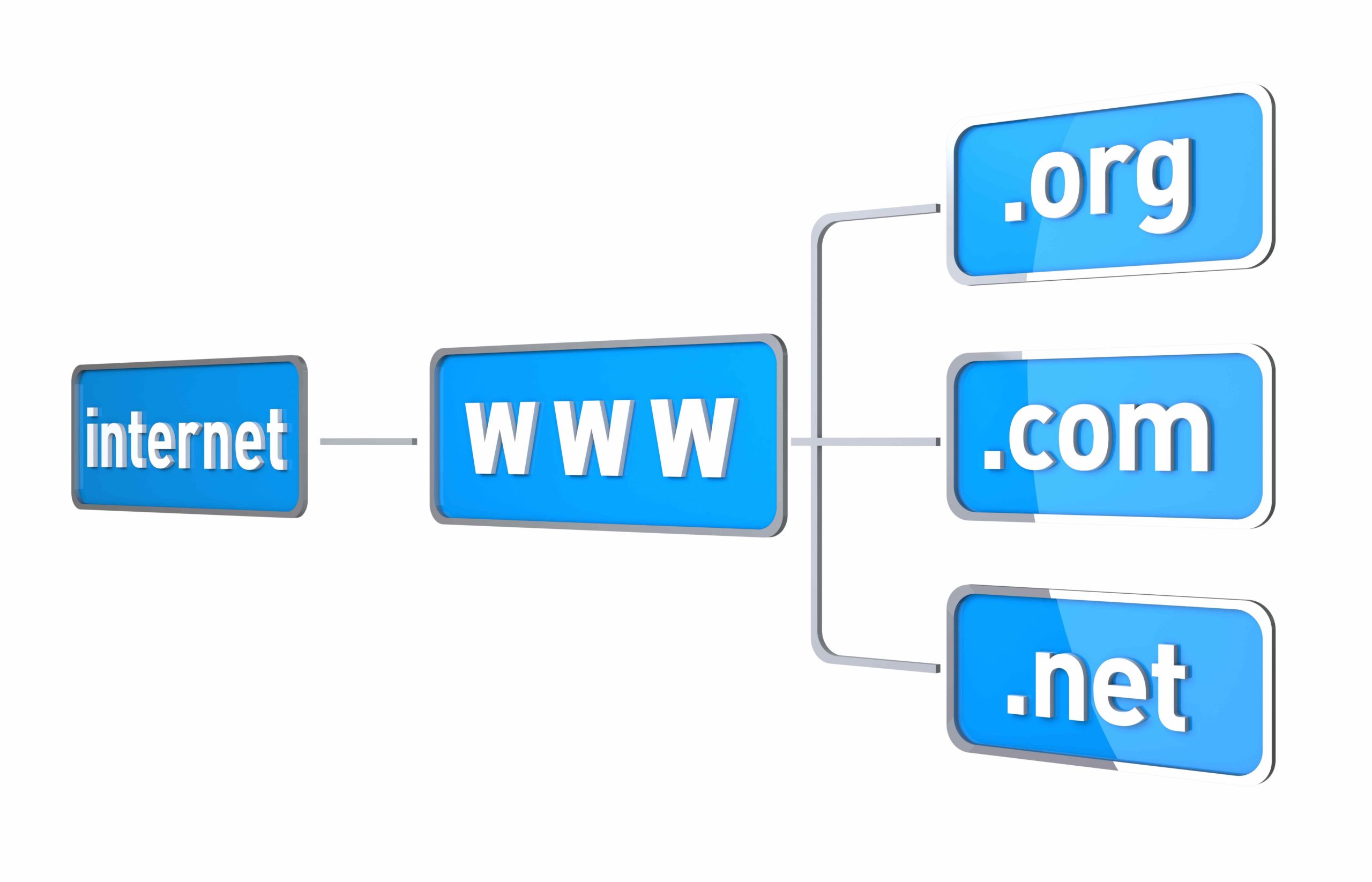
Differences between Root domains and Top-Level domains (TLD)
Root domains and top-level domains (TLDs) are essential components of a website’s domain structure. The TLD is positioned at the end of the URL, following the root domain. TLDs, like “.com,” “.org,” or country-code TLDs, provide information about the website’s nature or purpose.
In short, TLDs are used to classify and categorize websites, while root domains are used to organize and manage website content.
Setting Up the Root Domain
To set up a root domain, you can follow these basic steps:
Domain Registration
- Choose a domain registrar to register your desired root domain. Popular registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains.
- Search for available domain names, and once you find one, proceed with the registration process, providing the necessary contact information.
Choose a Hosting Provider
- Select a hosting provider to store your website files and data. Some well-known hosting providers are Bluehost, SiteGround, and HostGator.
- Purchase a hosting plan that suits your website’s needs. Many hosting providers offer packages that include a free domain registration.
Configure DNS Settings
- Access your domain registrar’s dashboard and locate the DNS (Domain Name System) settings or DNS management section.
- Set up DNS records, including A (Address) records, pointing to the IP address of your hosting server. Consult your hosting provider for the specific DNS settings.
Customize Settings
Once your domain is registered and hosting is set up, you can customize various settings, such as email forwarding, SSL certificate installation, and other domain-specific configurations based on your requirements.
Conclusion
A root domain is the foundation of a website’s address. It provides structure for subdomains and pages, impacting user experience and search engine rankings. Choosing a clear, memorable root domain and optimizing it for SEO is crucial for a strong online presence.